
Send encrypted logs to Graylog (Part 1: Linux machines)
This is the first part for Linux machines. The second part for Windows machines will follow soon.
The Graylog documentation unfortunately reads very contradictory and the Graylog error messages are hard to understand.The Graylog documentation unfortunately reads very contradictory and the Graylog error messages are hard to understand.To save others the trouble, here is a small howto:
Create shadow CA:
apt install openssl
mkdir /etc/graylog/server/ssl
cd /etc/graylog/ssl
# Create CA Keys
openssl genrsa -aes256 -out graylog-ca-key.pem 2048
openssl req -x509 -new -nodes -extensions v3_ca \
-key graylog-ca-key.pem -days 1024 \
-out graylog-ca-root.crt -sha512Activate your shadow root CA.Local CA repo on Debian/Ubuntu is /usr/local/share/ca-certificates
mv graylog-ca-root.crt \
/usr/local/share/ca-certificates/
# Activate your root CA:
update-ca-certificatesActiva root CA
Graylog needs a private key in PKCS8 format
openssl pkcs8 -in graylog.key -topk8 -out graylogPKCS8.keyCopy your JAVA keystore to /etc/graylog/server/cacerts.jks
[ -f /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/lib/security/cacerts ] \
&& cp /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/lib/security/cacerts \
/etc/graylog/server/cacerts.jksPlease note that in this example Java Open JDK 11 is used. The paths have to be adapted for 14 or later.
Import your shadow root CA to Elasticsearch:
keytool -importcert -alias graylogCA \
-keystore /etc/graylog/server/cacerts.jks \
-storepass changeit \
-file \
/usr/local/share/ca-certificates/graylog-ca-root.crtCreate Graylog Input
Create a new SSL TLS input in Graylog. Enclosed are the settings as text and as graphic.
allow_override_date: true
bind_address: 0.0.0.0
expand_structured_data: false
force_rdns: false
max_message_size: 2097152
number_worker_threads: 2
override_source: <empty>
port: 1515
recv_buffer_size: 1048576
store_full_message: false
tcp_keepalive: false
tls_cert_file: /etc/graylog/ssl/graylog.crt
tls_client_auth: disabled
tls_client_auth_cert_file: <empty>
tls_enable: true
tls_key_file: /etc/graylog/ssl/graylogPKCS8.key
tls_key_password: ********
use_null_delimiter: false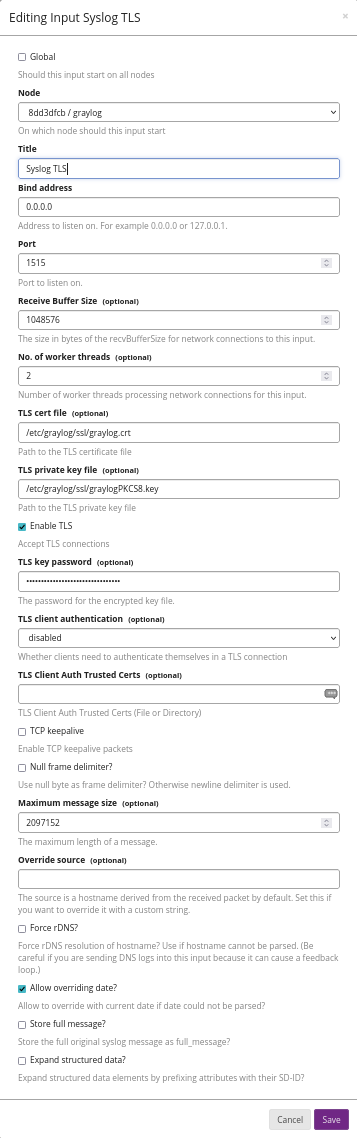
Client configuration
Copy the created Shadow Root CA to each machine that should send logs to Graylog (e.g. with SCP).
Install rsyslog and rsyslog-gnutls
apt install rsyslog rsylog-gnutlsConfigure graylog as a remote syslog server.
Create a new configuration file:
touch /etc/rsyslog.d/graylog.confAdd the following settings.
Replace GRAYLOGSERVERIP with your own server IP.:
*.* action(
Action.resumeInterval="10"
# cycling TCP connections allows for load balancing
RebindInterval="10000"
Queue.Size="100000"
Queue.DiscardMark="97500"
Queue.HighWaterMark="80000"
Queue.Type="LinkedList"
Queue.FileName="rsyslogqueue"
Queue.CheckpointInterval="100"
Queue.MaxDiskSpace="2g"
Action.ResumeRetryCount="-1"
Queue.SaveOnShutdown="on"
Queue.TimeoutEnqueue="10"
Queue.DiscardSeverity="0"
type="omfwd"
target="GRAYLOGSERVERIP"
protocol="tcp"
port="1515"
template="RSYSLOG_SyslogProtocol23Format"
StreamDriver="gtls"
# run driver in TLS-only mode
StreamDriverMode="1"
# host TLS cert CN will be used for authentication
StreamDriverAuthMode="x509/name"
# only allowed hosts
StreamDriverPermittedPeers="GRAYLOGSERVERIP"
)Restart rsyslog:
systemctl restart rsyslog.service